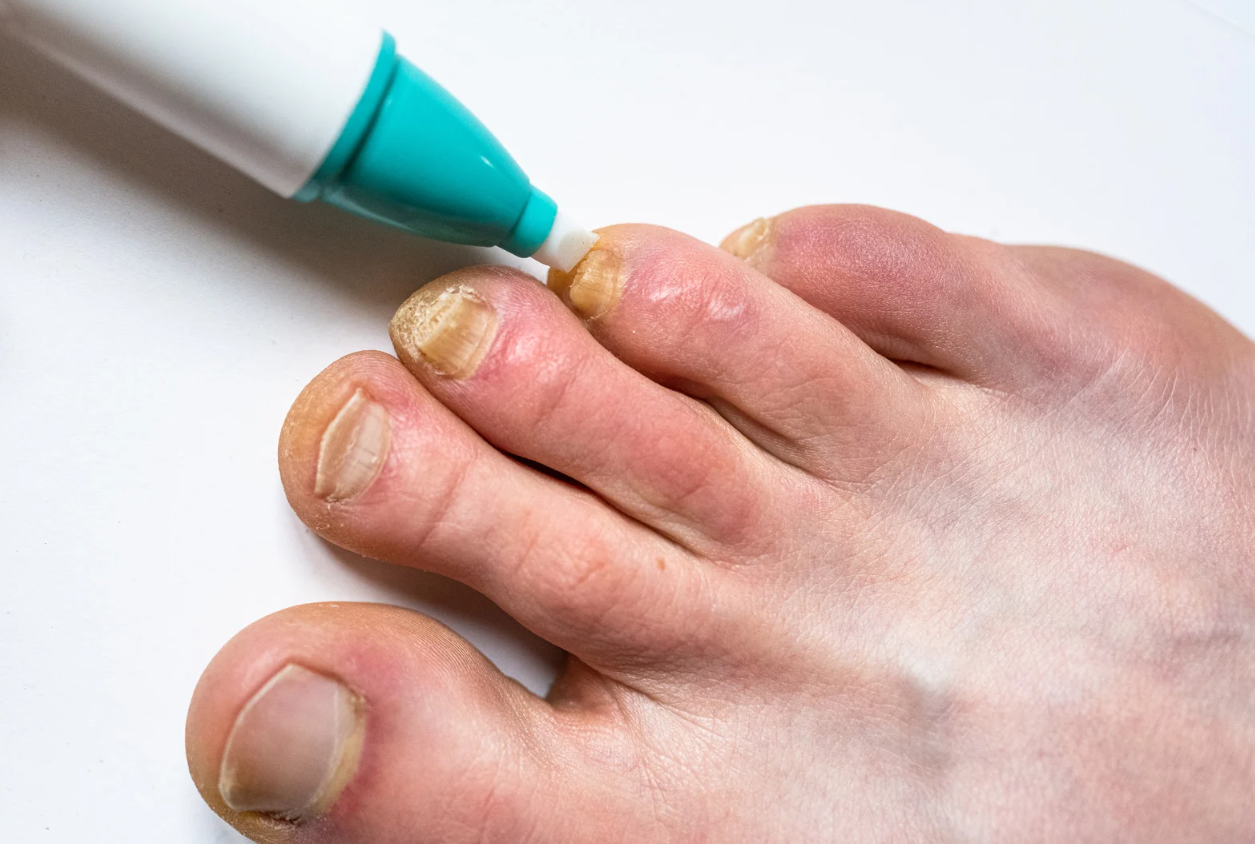
Fungal Toenails
Fungal toenail infection, also known as onychomycosis, is caused by fungi that typically enter through the tip of the nail, gradually spreading deeper into the nail. This infection leads to thickening, discoloration, nail separation, and a chalky appearance.
Fungal toenails affect 5-10% of the general population, with the prevalence rising to 20-30% among individuals over the age of 60. Men are also 1.5 to 2 times more likely to develop fungal toenails than women.
Fungal toenails can develop due to a variety of risk factors, including age, as the condition becomes more common over time. Being male also increases susceptibility, as does having a compromised immune system, which makes it harder to fight off infections.
Unhygienic nail salons can introduce fungi, while conditions like diabetes and reduced circulation can make the feet more vulnerable to infections.
Nail injuries or trauma can also pave the way for fungal growth, as can prolonged exposure to damp, moist environments. Poor foot hygiene and living in warm, humid climates further increase the risk of developing fungal toenails.